The primary reason that Blockchain offers the fastest transactions is due to its decentralized nature. There’s no intermediary involved in a transaction, so you save time and money. In the crypto world, smart contracts take over the role of lawyers and intermediaries. Smart contracts are computer-based protocols that verify and enforce the negotiation of a deal.
In the world of Blockchain, the third-party services that provide smart contracts with external information are blockchain oracles. They connect Blockchain with the outside world. In this article, we’ll discuss why scalability and interoperability, the two holy grails of Blockchain, depend on oracles.
Scalability means the capability of the Blockchain to manage increased workload, i.e., more transactions. On the other hand, the ability of different algorithms to exchange information and communicate with each other is called interoperability. The functioning of oracles involves providing interoperability between various blockchains.
Importance of Interoperability
As we know, cryptocurrencies use Blockchain technology. They have the advantage of not being under the control of any government or authority. But there remain some centralized failure points. The exchanges link the decentralized and centralized space. These links are not so secure and vulnerable to hacking attacks. The main hindrance before Blockchain is the ability to connect to financial institutions. It was initially perceived that one Blockchain would host a group of smart contracts. A smart contract in the Blockchain is a software program or a transaction protocol that can execute independently. The terms of the agreement in the smart contract are decentralized and written in the block itself.
After the development of Blockchain, users recognize the need for several smart contract platforms to get linked. So, for Blockchain to be functional for multiple uses, all these platforms must fully connect.
Types of Oracles
On-chain
This type of oracle bridges two different blockchains using the third Blockchain. Some applications like Wanchain, ICON, and AION use this method.
AION uses the Hub and Spoke method where the linking Blockchain behaves like a central Hub. The other two blockchains get connected to this Hub like spokes.
There are two other methods, viz. decentralized exchange and bridge. The decentralized exchange provides interoperability links between two different projects. And in the bridge method, the connecting Blockchain helps the other two blockchains to communicate freely.
Off-chain
Off-chain uses a middleware system and is of four different types of viz. Atomic Swaps, Operation System, State Channels, and Oracles.
Atomic swaps allow the exchange of two assets using a decentralized method. The operating system enables inter-chain messaging and atomic swaps together. State channels allow off-chain communication and atomic swaps. Oracles enable varied cross-communication amongst blockchains and enterprise systems or large-scale applications software bundles.
We can categorize oracles into software oracle and hardware oracle. Software oracles pass on information from online sources like websites or smart contracts or even backend APIs. Hardware oracle uses IoT devices like smartphones to track, verify, and then send data to smart contracts.
Why are Blockchain Oracles Required?
Smart contracts in blockchain technology can execute irreversible operations. For this reason, the information must come from a trustworthy source. The decentralized blockchains remain isolated from other sources of information. An oracle eliminates the chances of any incorrect data by linking the Blockchain to the real source of information. An example of buying insurance without getting cheated may be cited here. We can buy insurance over blockchains using oracles. The decentralization of Blockchain technology, combined with the reliability of oracle, can prevent fraud.
Reliability of Blockchain’s Oracle
The Oracle needs to be reliable for maintaining the security of the blockchains. Oracles primarily use the following four techniques to be trustworthy.
Multiple Source Data
The Oracle should collect information from different sources. This reduces the chances of getting incorrect information to zero.
Multiple oracles
Another method could be to collect information from other Oracles. This eliminates the single-point-of-failure that can arise if one Oracle works.
Incentive Mechanism
The Oracle may give an incentive in the form of tokens to honest information collecting nodes in the network. Now, a slashing protocol may punish the corrupt nodes.
Trusted Execution Environment (TEEs)
The Oracle may use a secluded environment or enclave to execute the information exchange or transactions. The enclave assures confidentiality and reliability without sharing the information with any third-party platform.
Pathbreaking Blockchain Oracle Programs
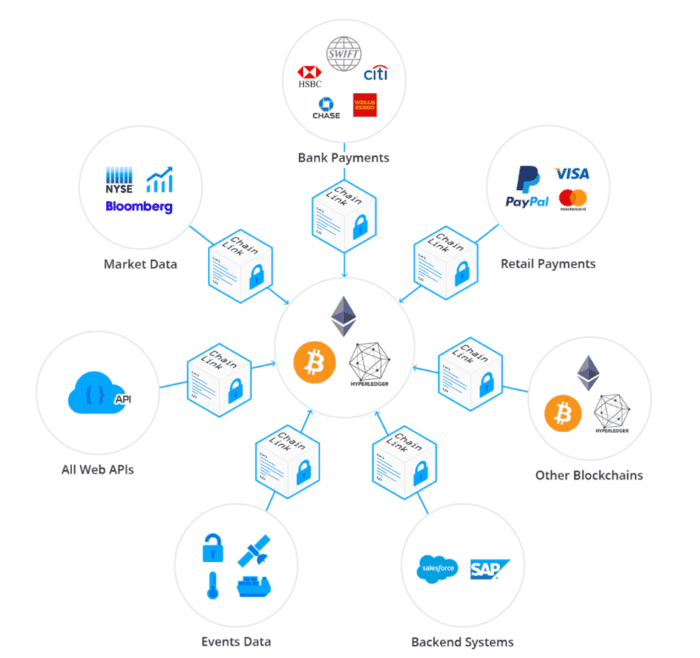
ChainLink
This is an innovative decentralized oracle network used with Ethereum blockchain. It focuses on connecting the blockchains of Bitcoin, Hyperledger, and Ethereum.
Augur
Augur, a decentralized prediction market protocol is built on the Ethereum platform. This Oracle allows a user to buy and sell shares by speculating the market. The market speculations are made on the outcome of an event like the result of a basketball game.
RIF Gateways
Also known as Rootstock, it connects Bitcoin’s Blockchain through sidechain technology. It allows users to create apps that can be compatible with Ethereum and have Bitcoin Blockchain’s security protocols.